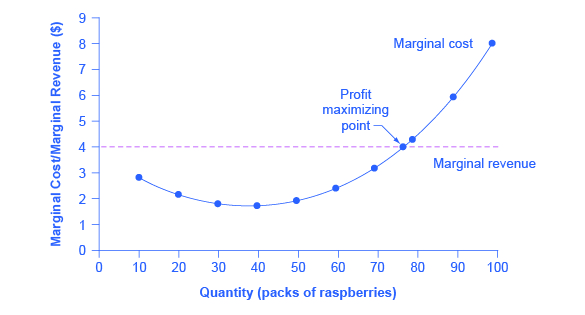
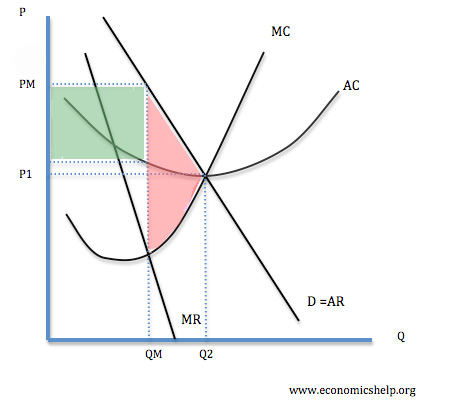
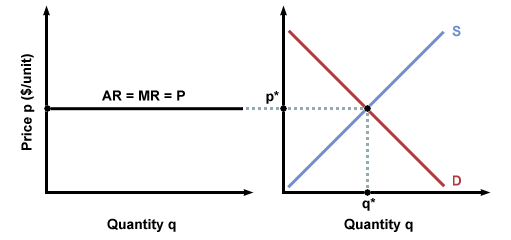
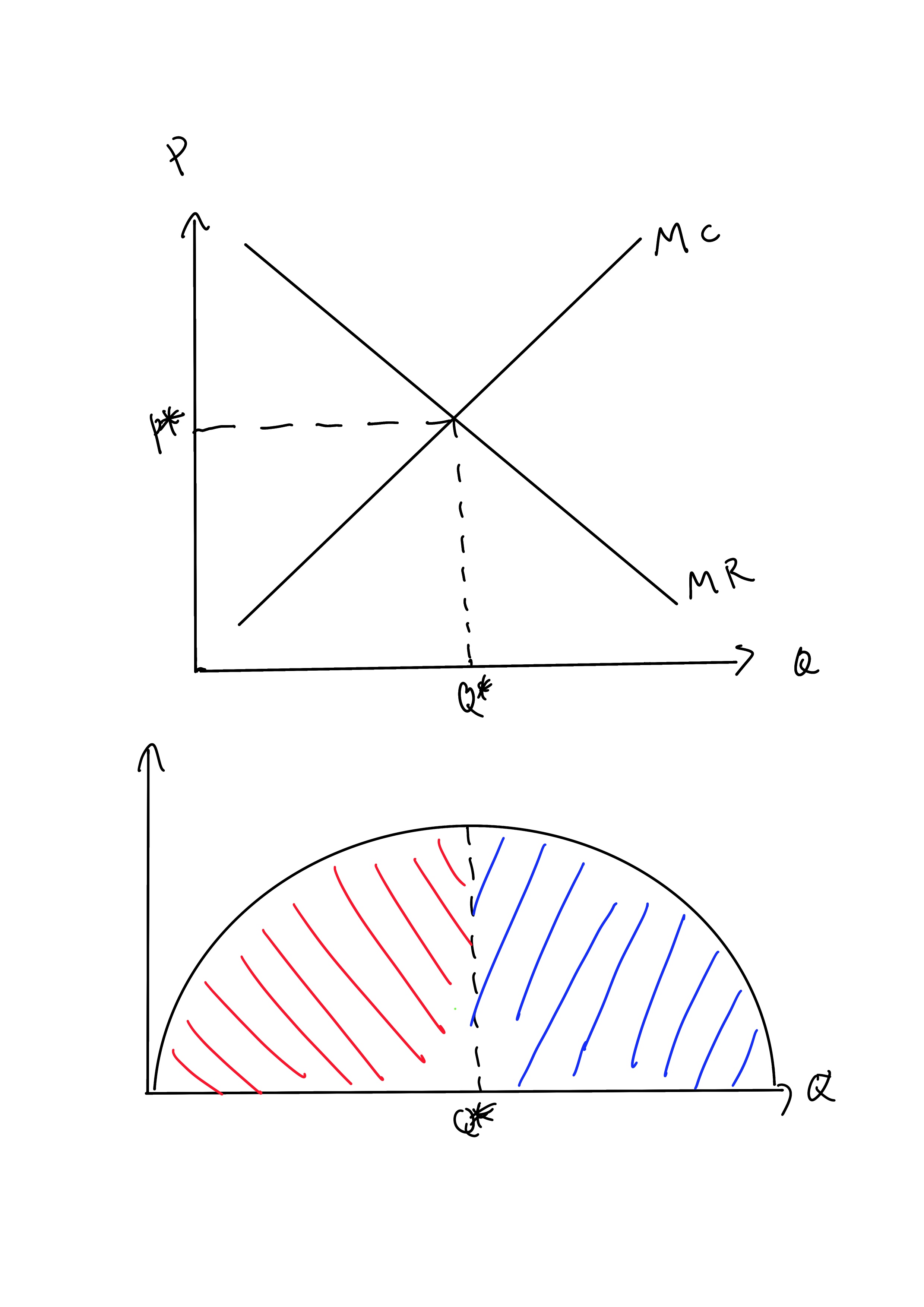
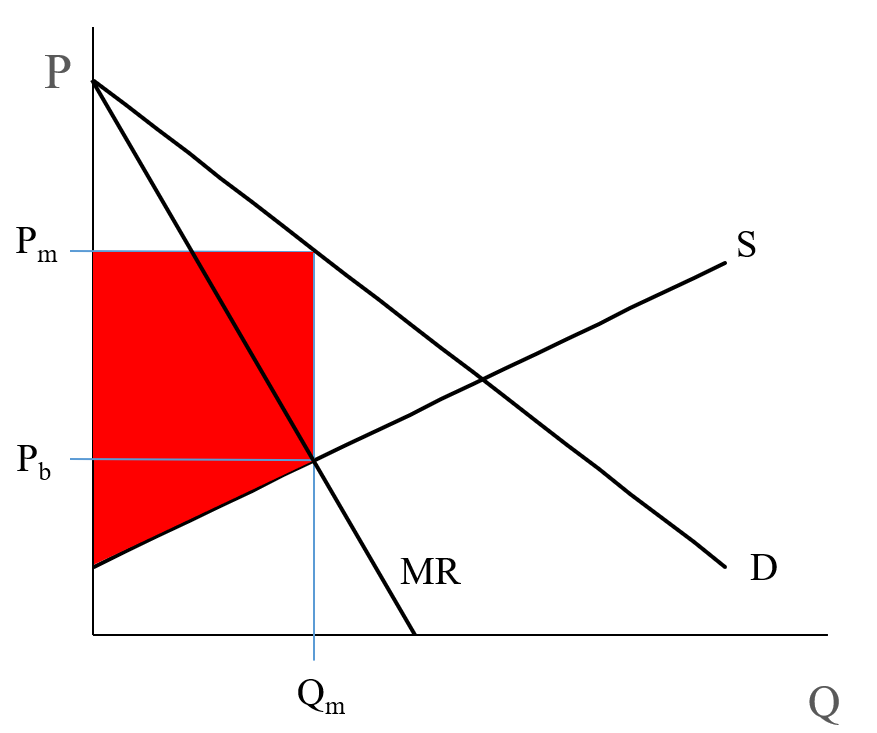
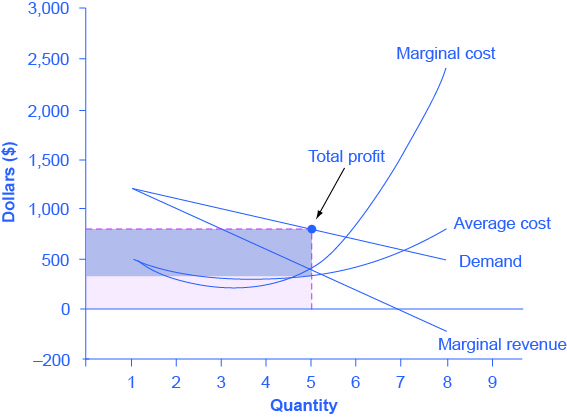
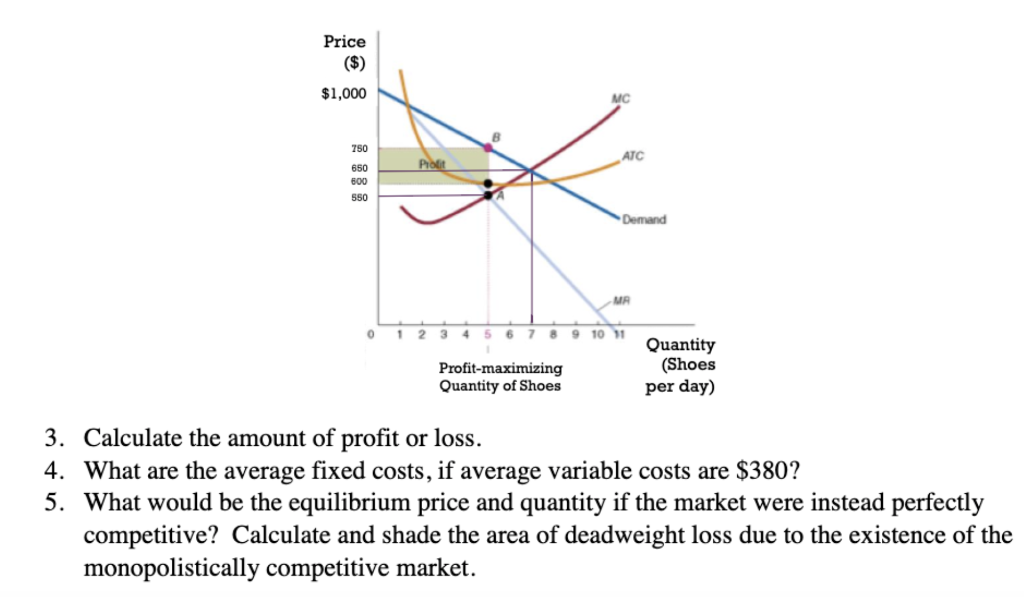
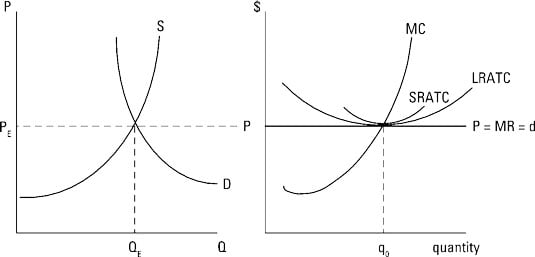
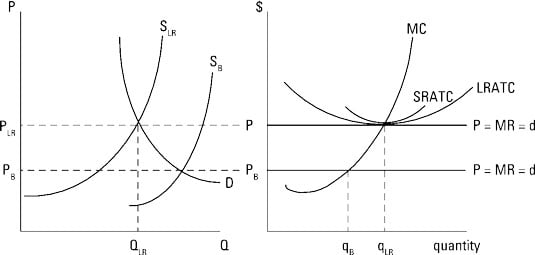
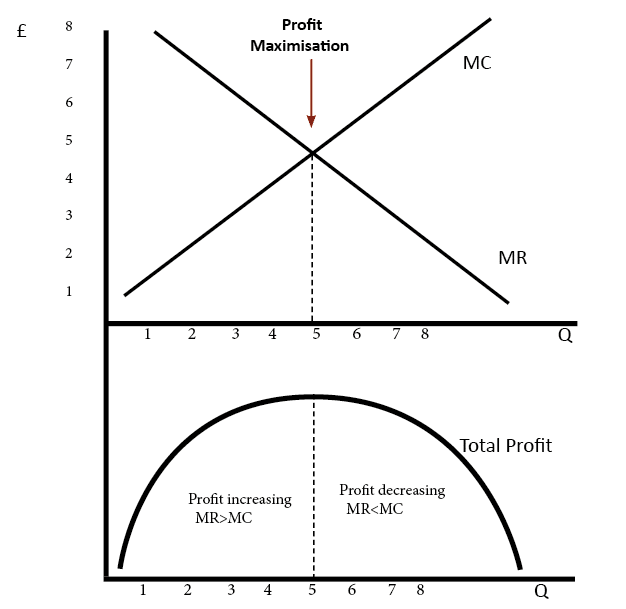
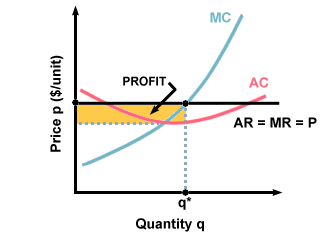
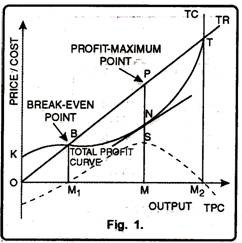
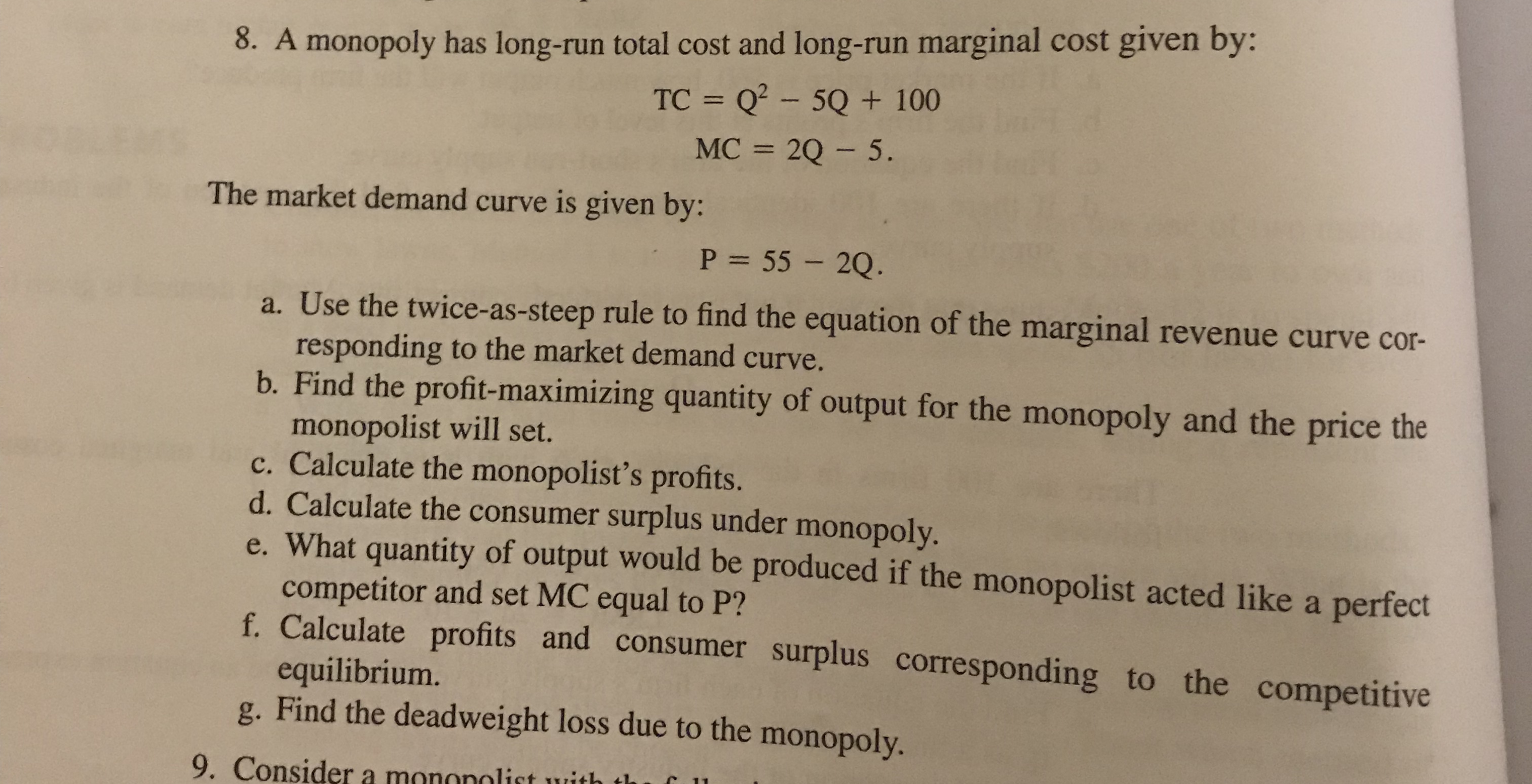a. What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing output and price? b. Calculate the monopolist's profit/loss, if any. c. What combination of output and price would be produced in this market if it were

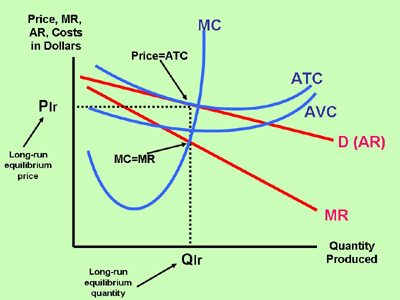
Section 2: Short-Run and Long-Run Profit Maximization for a Firm in Monopolistic Competition | Inflate Your Mind

profit maximizing level of price and output from demand functions of two goods . finding revenue - YouTube