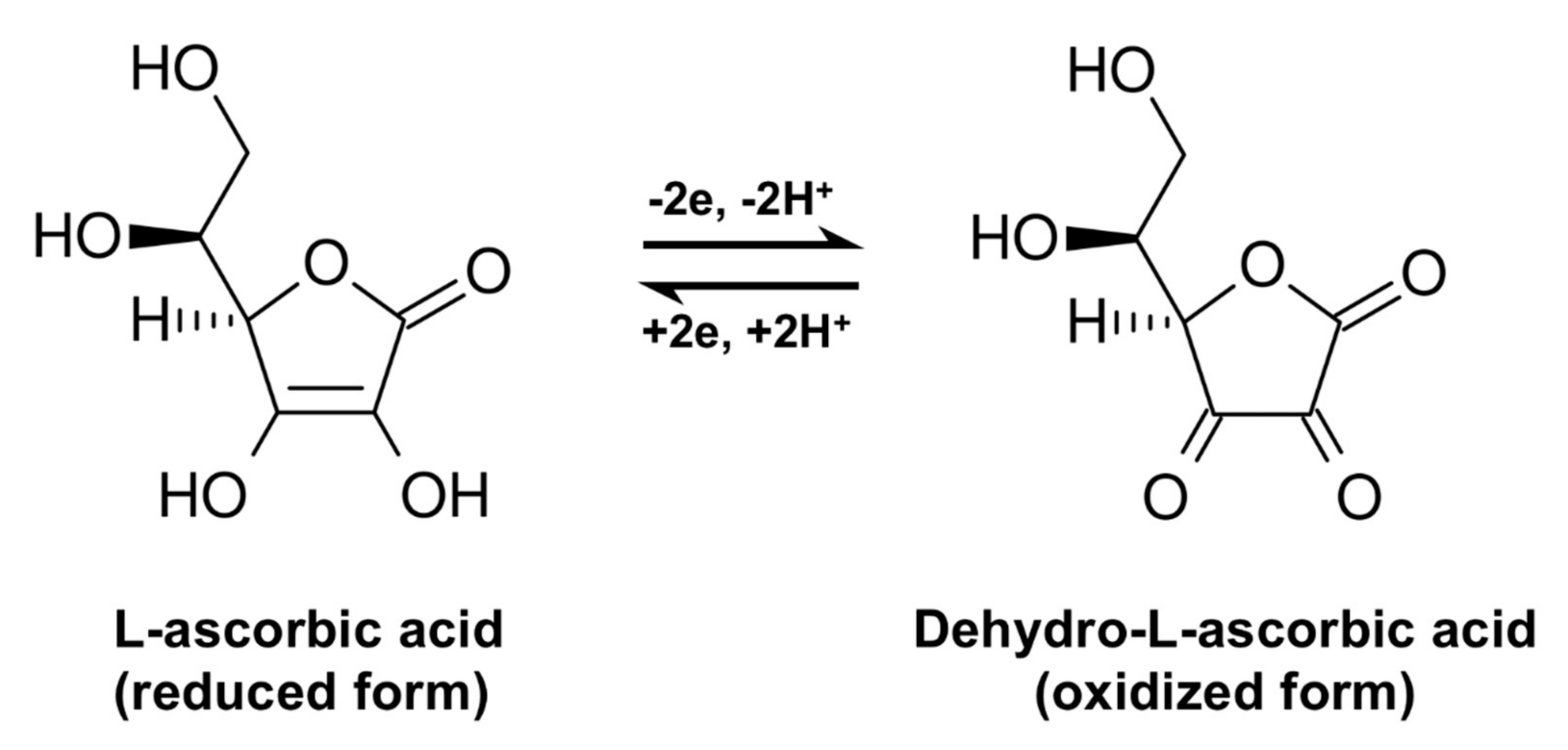
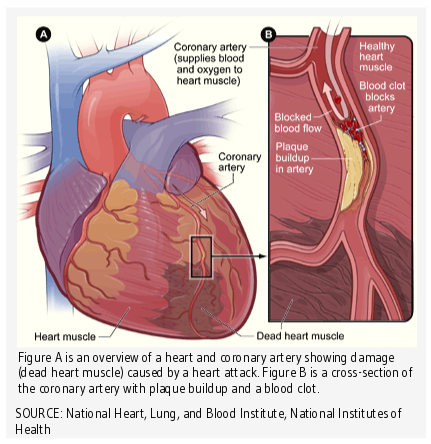
Vitamin D, Calcium Supplements, and Implications for Cardiovascular Health: JACC Focus Seminar | Journal of the American College of Cardiology

The relationship between vitamin C status, the gut-liver axis, and metabolic syndrome - ScienceDirect
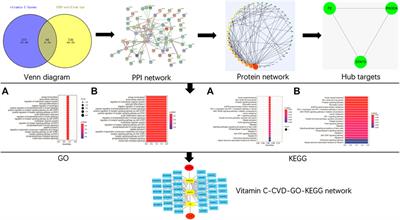
Frontiers | Targets of Vitamin C With Therapeutic Potential for Cardiovascular Disease and Underlying Mechanisms: A Study of Network Pharmacology
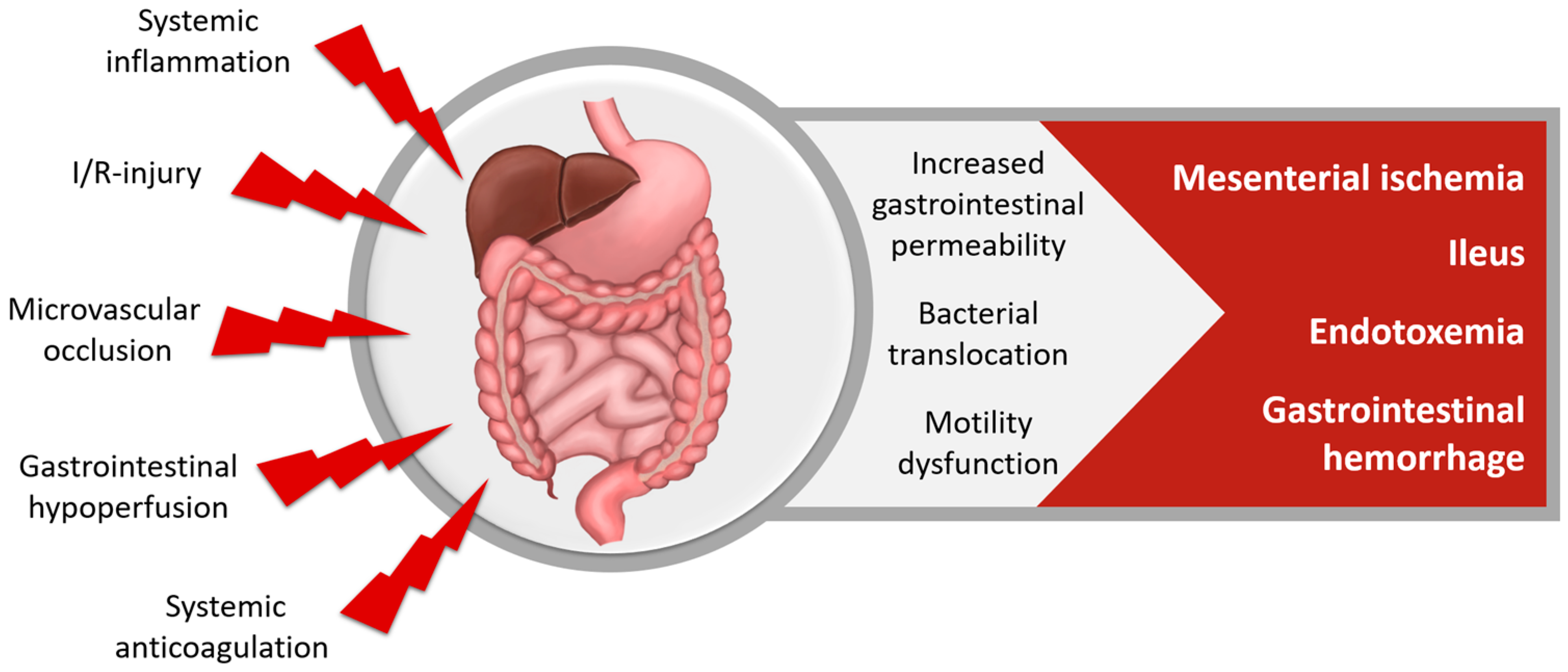
Nutrients | Free Full-Text | Vitamin C to Improve Organ Dysfunction in Cardiac Surgery Patients—Review and Pragmatic Approach